Application performance management (APM) tools are commonly used to monitor, manage, and/or maintain the performance and availability of software applications. Modern businesses rely on many APM tools to reliably deliver mission-critical applications to end users.
The specific functions of an APM tool can vary, but examples of APM functionalities include:
- Application Event Alerts. APMs with this functionality alert application managers of specific events related to the application, such as dips in application performance, unauthorized login attempts, when peak traffic load has been reached, and more. The alerts provided vary from one APM solution to the next, and many APMs allow these alerts to be customized to the business’s needs.
- Network Health Monitoring. Some APMs allow for monitoring of the network environment. Network health monitoring can help application owners identify potential issues that could lead to a network outage, and aid in weighing load balancing by letting managers redirect incoming connection requests away from overloaded application servers to less overwhelmed ones.
- Application Log Filing. How many connection requests has your app processed in the last few days? How many server timeouts did end users experience on average over the last week? How many illicit access attempts were made, which devices were they made on, and where were these devices connecting from? These are all questions that should be answered by an APM’s application log filing feature. The forensic data that these features collect is vital for identifying weaknesses in the application’s security or design for future repair.
- End User Experience Monitoring. This APM feature is closely related to application log filing, but focuses its monitoring metrics on the how the end user’s experience is impacted by server lag, user interface quirks, and so on. This particular APM tool is highly useful to companies with outward-facing applications meant for consumers. However, companies with inner-facing employee apps also benefit from this, as improving user experience increases adoption of business apps by employees.
To gather all of these APM features, organizations commonly use an APM tool like the Netscout Infinistream. This out-of-band APM tool needs a visibility fabric from Gigamon or Ixia to aggregate and filter the traffic and send it to the Infinistream. Five years ago this was a cleaver way of getting visibility into the performance of you apps but today it is very expensive and complex solution. Now, you don’t need more tools and you don't need the aggregation and filtering layer to get traffic to those tools. You just need a smart load balancer.
The Benefits of A SMART LOAD BALANCER
The Avi Vantage Platform is a smart, software-defined load balancer that separates the control plane from the data plane. This modern architecture enables features that go beyond load balancing to include application performance monitoring, multi-cloud traffic management, predictive autoscaling, security, and container services for bare metal, VM, public cloud, containers, and PaaS environments. Here are a few of the things that Avi’s elastic load balancing solution can do that contribute to the same goals usually fulfilled by a dedicated APM tool:
- Fast Rollout for Applications and New Services. As Avi Vantage enables automation for app provisioning using a software-based system (with out-of-the-box integrations with SDN, OpenStack, and container technologies), the provisioning time for app rollout shrinks from weeks to hours. Multitenancy support with virtual machines makes it easy to isolate applications for easy upgrades and minimize other delays.
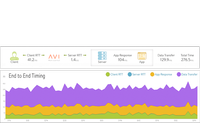
- Rapid Incident Resolution. Select features, such as at-a-glance views of all virtual services throughout the system, enable users to see every aspect of the network and get alerts that enable swift incident resolution. By collecting real-time application telemetry from distributed service delivery points (i.e. the Avi Service Engines), granular, real-time insights into application health and information transactions can be achieved.
- Continuous Integration/Deployment (CI/CD) with Free Licenses for Dev and Test Environments. Developers can build services into their apps to test performance and stability without disrupting active environments by taking advantage of Avi Vantage’s free licenses for dev and test environments.
- Application Isolation and Health Monitoring. Vantage’s built-in security features application isolation with micro-segmentation for East-West security — compartmentalizing the network for greater monitoring power. Additionally, the admin console displays security information about SSL versions and ciphers used in transactions, as well as system health scores calculated in real time.
- L4—L7 Policies. Layer 4 – layer 7 security policies, such as URL filtering, application allowlisting, and application denylisting, help keep applications secure from intrusion attempts. Such security helps maintain application stability and prevent data breaches—all with a single point of control.
- Network “DVR.” Vantage keeps an active log of application and network events that application managers can use to replay such events and pinpoint key app issues. This helps with forensic examinations of app data in case of failure, so the cause can be quickly determined and remedies made.
- App Maps with Visual Interactions. Simple GUIs make for better management tools, period. Avi’s load balancing solution leverages easy-to-use app maps with visual interactions to keep app management as simple as possible for managing microservices.
By utilizing a modern software-defined architecture you can realize significant cost savings by not having to buy additional APM tools. Discover the benefits of Avi’s elastic load balancer for yourself by checking out this case study, or see what you could save with our TCO calculator.